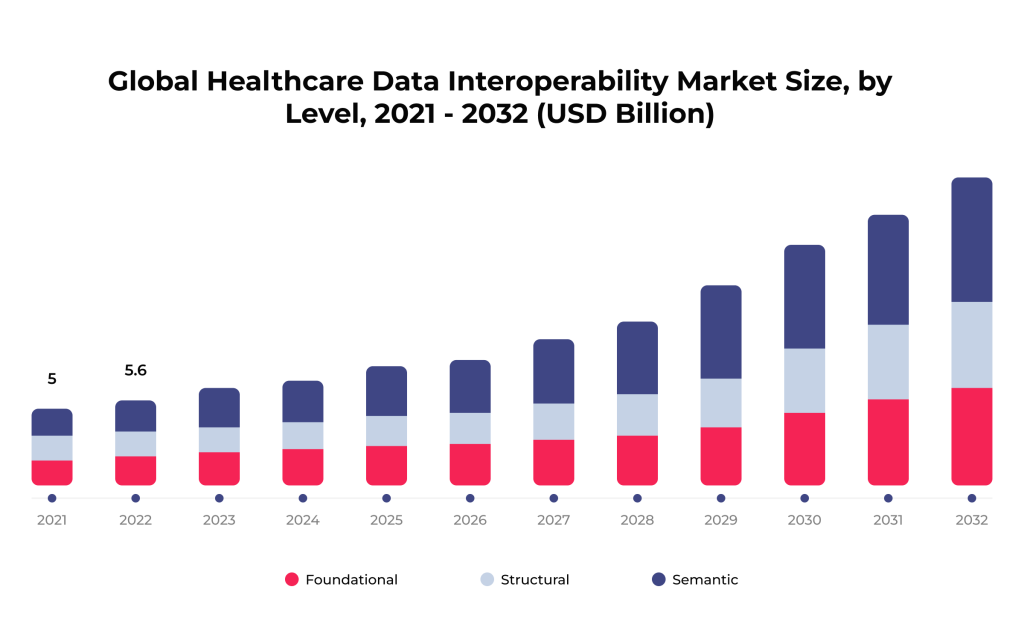
In the dynamic world of healthcare, the power and potential of data are becoming increasingly evident. In 2022, the healthcare data interoperability market was valued at over $5.5B and is expected to keep increasing over the next few years.
From enhancing patient care to streamlining administrative processes, the role of data in transforming the medical landscape is undeniable. This article delves into the impact of healthcare data interoperability, its levels, benefits, challenges, and accepted standards. Also, we are discussing tips medical facilities can use to improve seamless data exchange and five burning trends in this niche.
Table of Contents
“Our healthcare data interoperability services ensure seamless communication across various healthcare systems, enhancing patient care and provider efficiency. SPsoft team’s commitment to delivering customized, cutting-edge solutions has enabled us to empower healthcare practices and patients. Being a part of this journey, where we bridge gaps in healthcare data exchange, is incredibly fulfilling.”
Romaniya Mykyta
Head of Product Management, SPSoft
“At SPsoft, we pioneered solutions enabling seamless healthcare data interoperability across systems, leading to improved patient outcomes and streamlined provider workflows. Our innovative approach has set new standards in the industry. So, I am proud to lead a team at the forefront of enhancing healthcare efficiency through advanced data-sharing technologies.”
Mike Lazor
CEO, SPSoft
Why Is Healthcare Data Interoperability Important?
In today’s complex and data-rich medical landscape, healthcare data interoperability is essential for leveraging the full potential of digital health techs. That leads to better health outcomes and a more efficient healthcare system. Thus, healthcare interoperability is vital for some key reasons.
Patient-Oriented Impact
When it comes to patient care, seamless data exchange is pivotal in reshaping the patient experience. Here are some of the effects it has.
Better Patient Care
Data interoperability in healthcare allows for seamless exchange and interpretation of patient data across healthcare systems. It ensures that healthcare providers can access a patient’s complete health history, like diagnoses, medications, lab results, and past treatments. Such an approach is crucial for accurate diagnosis, treatment planning, and avoiding medical errors.
Patient Empowerment
Interoperability can give patients more access to and control over their health information. That can lead to greater patient engagement in their care, better adherence to treatment plans, and more informed decision-making.
Improved Public Health
Interoperable systems allow for easier aggregation and analysis of health information, which is invaluable for tracking public health trends, managing outbreaks, and conducting research. That can result in better-informed public health policies and more effective healthcare strategies at a population level.
Impact on Operations
On the operational front, healthcare data interoperability is a key driver for the efficiency of medical services. Here are some of the impacts an organization’s operations may experience.
Enhanced Efficiency
When healthcare systems are interoperable, that reduces the time and resources spent on administrative tasks, such as manually transferring patient records or re-entering data. This efficiency can promote cost savings for healthcare providers and payers and faster, more streamlined patient care.
Coordinated Care
In cases where a patient is seeing multiple specialists or transitioning between care settings (e.g., hospital to home care), data interoperability ensures that all healthcare providers are on the same page. This coordinated approach can improve outcomes and patient satisfaction.
Compliance and Standardization
Healthcare data interoperability requires adherence to specific standards and regulations, which can increase healthcare systems’ overall quality and safety. That also ensures compliance with legal rules related to patient data and privacy.
Innovation and Future Healthcare Models
Interoperability paves the way for innovative healthcare delivery models like telemedicine, remote patient monitoring (RPM), and personalized medicine. By facilitating the seamless data exchange, new technologies can be more effectively integrated into healthcare.
Healthcare data interoperability is crucial for delivering high-quality, efficient, and coordinated care. That leads to numerous benefits, such as enhancing the patient experience, improving public health outcomes, and driving innovation in the industry.
Have specific questions on healthcare data interoperability? Contact us directly to discuss your organization’s progress with seamless data exchange!
Levels of Data Interoperability in Healthcare
Healthcare data interoperability can be understood at different levels, representing a more advanced integration stage and communication capabilities. They are typically categorized as follows.
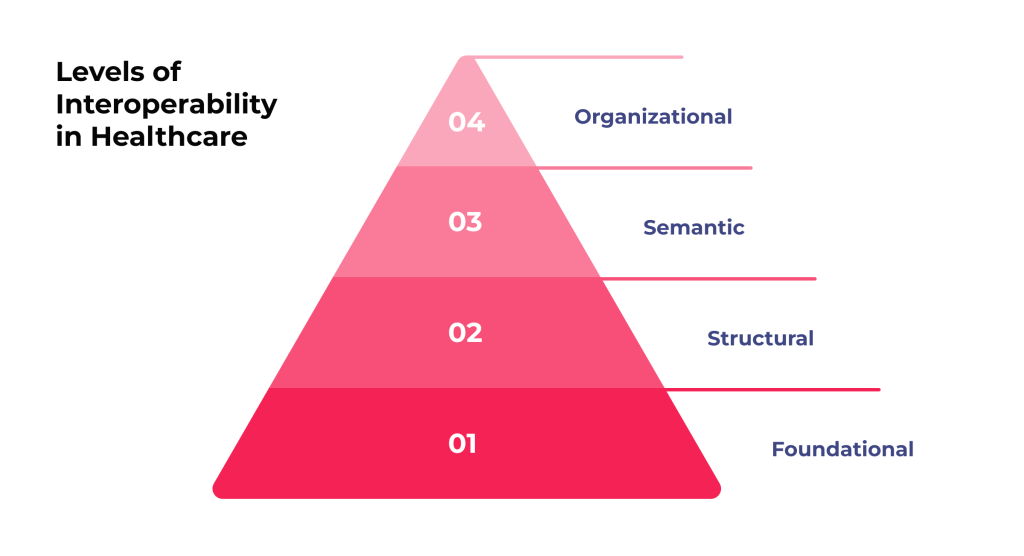
1. Foundational Interoperability
That is the most basic level of interoperability. It allows data exchange from one information technology system to another. However, the receiving system does not need to interpret the data at this level. For example, a lab system might send test results to a hospital’s electronic health record (EHR) system, but the EHR system may not be able to interpret or process the information beyond simply displaying it.
2. Structural Interoperability
This level is a step up from foundational healthcare data interoperability. It defines the structure or format of data exchange, ensuring that data between information systems can be interpreted at the data field level. That involves uniform movement and presentation of information, such as consistently structured healthcare messages. Besides, this interoperability level allows different systems to interpret and use the data meaningfully and accurately.
3. Semantic Interoperability
That is the highest level of interoperability, involving data exchange between systems and its further meaningful and accurate interpretation and usage. Semantic interoperability requires data to be codified using standardized terminologies like SNOMED CT and LOINC. This level is essential for enabling advanced functions such as clinical decision support, data analytics, and fully coordinated patient care across different healthcare settings.
4. Organizational Interoperability
While only sometimes listed as a separate category, this level goes beyond the tech aspects of data exchange. It focuses on the governance, policy, social, legal, and organizational nuances that facilitate the secure, seamless, and timely communication and use of data between medical facilities. This level considers factors like data-sharing agreements, alignment of incentives, and workflow optimization to support healthcare data interoperability at a larger scale.
After all, these levels build upon each other, each adding more complexity and functionality. Achieving higher levels of healthcare data interoperability can greatly enhance the efficiency of healthcare delivery, leading to improved patient outcomes and more coordinated care.
Curious about how healthcare data is collected to drive informed decisions? Our comprehensive article provides an in-depth exploration of the relevant processes!
Benefits of Integrating Healthcare Data Interoperability
The significance of data interoperability in healthcare extends well beyond the realms of information exchange and technology. Let us explore its benefits in detail:
Advantages for medical institutions:
- Facilitates Multidisciplinary Care. Healthcare data interoperability guarantees that all providers can access the same information for patients with complex conditions requiring multiple specialists. That facilitates a more cohesive and holistic treatment approach.
- Supports Home and Community-Based Care. Interoperability is critical in supporting the shift towards home-based and community-centered care models. That allows for continuous monitoring and managing health conditions outside traditional settings.
- Optimizes Resource Allocation. By providing a clearer picture of patient flows and health trends, interoperability helps healthcare systems allocate better resources, plan services, and manage capacity, especially during peak demand periods or health crises.
- Drives Consumer-Centric Innovations. Interoperable data enables the development of new consumer-focused health applications and techs, giving patients more control over their health and wellness.
Advantages for patient engagement:
- Reduces Healthcare Disparities. Interoperability helps bridge healthcare access and quality gaps, especially in underserved or rural areas. By sharing information seamlessly, providers can ensure that all patients receive the same level of informed care, regardless of location.
- Enhances Emergency Response. In emergencies, having immediate access to a patient’s medical history can be crucial. Healthcare data interoperability ensures that emergency responders and ER doctors have the information to make rapid, informed decisions.
- Promotes Patient Data Portability. Patients can move between healthcare providers or geographies without the risk of losing their medical history. That is because interoperable systems allow for easy transfer and access to their health records.
- Improves Health Literacy and Engagement. When patients have access to their health data through interoperable systems, they are more likely to understand their health conditions and be engaged in managing their health.
These unique benefits highlight how healthcare interoperability extends beyond clinical outcomes, impacting patient empowerment and broader health system optimization.
Challenges in the Healthcare Data Interoperability Market
Achieving data interoperability in healthcare is a complex yet vital goal, covering more than just integrating technology. It involves navigating various challenges that span healthcare’s tech, regulatory, organizational, and cultural aspects. These challenges stem from a variety of factors:

Data-connected challenges:
- Diverse data standards. A great barrier is the lack of universally adopted standards for data formatting, structure, and semantics. Healthcare systems often use varied coding systems and data structures, making it difficult to achieve seamless data exchange.
- Data privacy and security concerns. Ensuring the privacy and security of patient data during exchange is paramount. Complying with regulations like HIPAA in the US, GDPR in Europe, and other regional data protection laws while maintaining data interoperability adds a layer of complexity.
- Variability in data quality and completeness. The quality and completeness of data in electronic health records (EHRs) can vary significantly. So, only accurate, complete, and updated information can ensure the effectiveness of interoperable systems.
- Patient data ownership issues. Determining who owns patient data and who is authorized to access or share it can be complicated, especially when multiple entities are involved in a patient’s care.
Organiztional and other chalanges:
- Legacy systems. Many medical providers use outdated IT systems not designed for healthcare data interoperability. Upgrading or integrating legacy platforms with newer, interoperable technologies can be costly and complex.
- Organizational and cultural barriers. Healthcare organizations often operate in silos, with different levels of willingness to share data. There can be resistance to change, lack of trust, or competitive concerns that hinder collaboration and data sharing.
- Cost and resource constraints. Implementing interoperable systems needs investment in techs, training, and ongoing maintenance. These costs can be prohibitive for many healthcare organizations, particularly smaller practices or those in low-resource settings.
- Lack of technical expertise. The technical expertise required to adopt and manage interoperable healthcare systems is not always available within medical organizations. That can lead to reliance on external vendors and customization or integration issues.
- Regulatory and policy limitations. The regulatory environment surrounding healthcare is complex and fragmented, with varying requirements across regions and countries. Navigating them while striving for healthcare data interoperability can be challenging.
Addressing these problems requires coordinated efforts among healthcare providers, IT experts, policymakers, and other stakeholders. Despite the obstacles, the push toward interoperability is critical for advancing a more efficient, effective, patient-centered healthcare system.
Looking to enhance your understanding of healthcare data management? Delve into our insightful article that covers all aspects of managing medical information!
Standards Regulating Data Interoperability in Healthcare
Healthcare data interoperability relies on adopting various standards that ensure information can be effectively shared and understood across different systems. Some key ones include:
- HL7 V2 and V3 are widely used for clinical and administrative data exchange. HL7 V2 is known for its ease of implementation, while HL7 V3 offers more rigorous specifications.
- FHIR (Fast Healthcare Interoperability Resources) is a newer standard that combines the best features of HL7’s earlier versions with web technologies. It is designed for ease of implementation and is suitable for many applications, involving mHealth apps, cloud communications, EHR-based data sharing, etc.
- DICOM (Digital Imaging and Communications in Medicine) is primarily used for imaging data, such as X-rays, MRIs, and CT scans. DICOM ensures that these images and related information can be shared and viewed consistently across different systems.
- LOINC (Logical Observation Identifiers Names and Codes) are used for lab tests and clinical observations to standardize the identification of measurements, observations, and documents.
- SNOMED CT (Systematized Nomenclature of Medicine — Clinical Terms) is a comprehensive clinical terminology that provides a common language for clinical terms, enabling consistent data capture, sharing, and retrieval.
- ICD (International Classification of Diseases) is used for diagnoses and procedures. ICD codes are critical for billing, epidemiology, and research.
- CDA (Clinical Document Architecture) is a standard that specifies the structure and semantics of clinical documents for exchange.
- CCD (Continuity of Care Document) is based on CDA. CCD provides a standard for summarizing a patient’s clinical, demographic, and administrative information for efficient data exchange.
- NCPDP (National Council for Prescription Drug Programs) specializes in standards for pharmacy services, including e-prescribing and medication history.
- X12N Health Care Transactions are used for administrative and financial transactions, such as billing and claims processing.
- IHE (Integrating the Healthcare Enterprise) is not a standard but a framework that specifies how to use existing standards like DICOM and HL7 to improve data exchange.
These standards are critical for enabling healthcare systems and applications to work together effectively. Adopting them is critical to achieving true healthcare data interoperability.
5 Tips to Improve Healthcare Data Interoperability
Improving the interoperability of data in healthcare is a multi-faceted challenge that requires strategic planning and execution. Here are five tips that can help organizations enhance their interoperability capabilities.
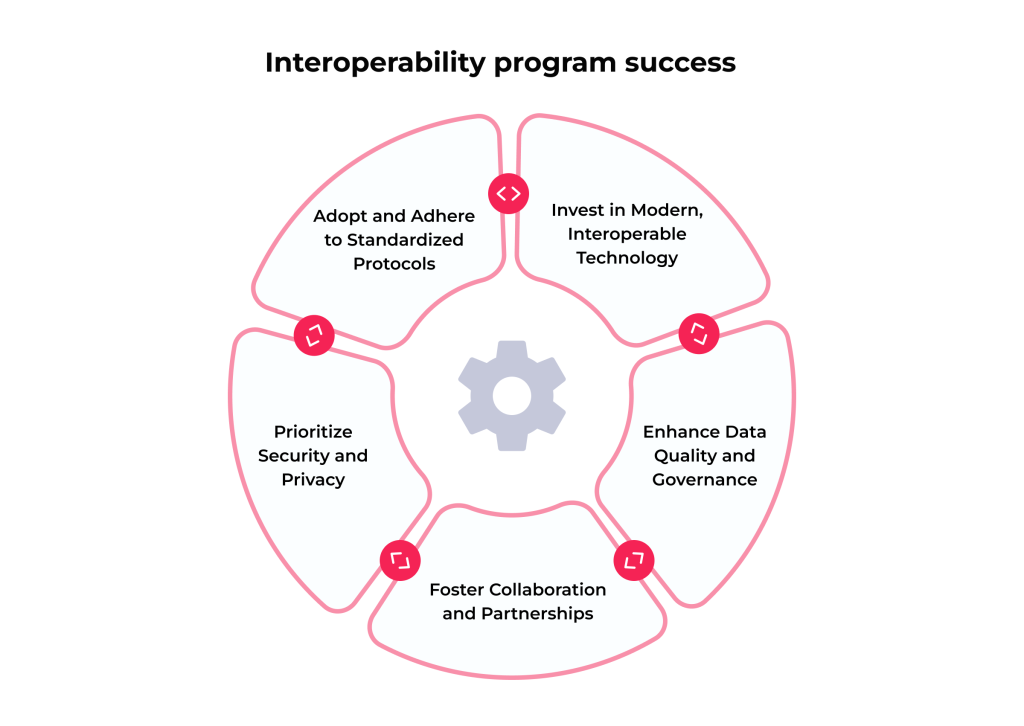
1. Adopt and Adhere to Standardized Protocols
Embrace widely recognized data standards like HL7, FHIR, DICOM, LOINC, and SNOMED CT. Consistent use of these standards ensures that you can effectively share and interpret data across different systems and organizations. Additionally, regularly update systems to comply with the latest versions of these standards.
2. Invest in Modern, Interoperable Technology
Replace or upgrade legacy systems that are not conducive to healthcare data interoperability. Investing in modern tech solutions built with data interoperability in mind, such as cloud-based platforms and FHIR-based EHR systems, can significantly improve data exchange capabilities.
3. Enhance Data Quality and Governance
Ensure that the information being shared is accurate, complete, and up-to-date. Adopt robust data governance policies to maintain the integrity and quality of the data. That includes regular audits, validation checks, and guaranteeing data entry is standardized across the organization.
4. Foster Collaboration and Partnerships
Work collaboratively with other healthcare settings, tech providers, and industry groups. Sharing best practices, resources, and experiences leads to more effective health data interoperability solutions. Participating in health information exchanges (HIEs) can facilitate better data sharing and integration.
5. Prioritize Security and Privacy
As healthcare data interoperability increases, so does the risk of data breaches and privacy violations. Implement strong security measures such as encryption, access controls, and regular security audits. Ensure compliance with relevant regulations like HIPAA in the United States or GDPR in Europe to protect patient privacy.
By focusing on that, healthcare organizations can make strides in improving interoperability, leading to better patient care, enhanced efficiency, and more effective use of healthcare data.
5 Recent Trends in the Healthcare Data Interoperability Market
The landscape of healthcare data interoperability is rapidly evolving, driven by technological advancements and the growing need for more integrated healthcare systems. Here is a look at some of the latest trends shaping this field.
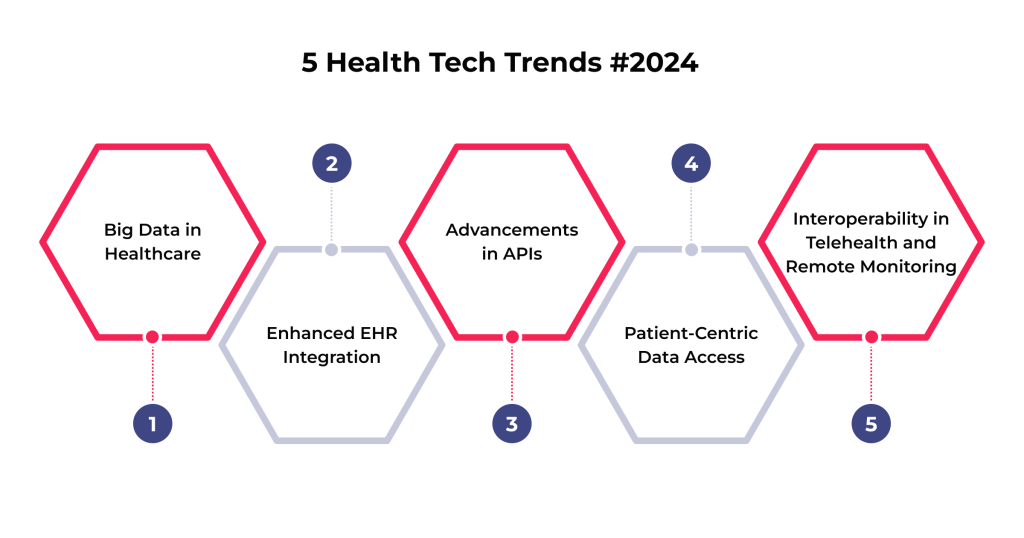
Big Data in Healthcare
The surge in healthcare-related data from various sources like EHRs, wearable devices, and genetic testing has brought big data to the forefront of healthcare. Big data analytics are used to derive meaningful insights from vast and diverse healthcare datasets. This trend is:
- enhancing patient care
- streamlining operational efficiencies
- facilitating groundbreaking research in predictive analytics and personalized medicine
The challenge lies in harnessing this data in a way that respects privacy and security while providing actionable insights.
Enhanced EHR Integration
EHRs are becoming more sophisticated and integrated — over 90% of US hospitals use the relevant platforms today. The focus is now on enhancing EHR systems for more seamless interoperability between healthcare providers. That includes improving user interfaces for better clinical workflows and integrating decision support tools directly into EHRs.
The goal is to make EHRs more than just digital records but a central hub for complex patient care management. This integration includes various health IT systems, ensuring patient data is accessible and usable across different care settings.
Advancements in APIs
Application Programming Interfaces (APIs) are crucial in the health data interoperability landscape. They facilitate the connection between healthcare systems and applications, enabling them to communicate and share data more efficiently.
The emergence of FHIR standards has been a game-changer in this space. FHIR-based APIs are designed to be simpler to implement and more user-friendly, enhancing the ability of healthcare apps to access data from EHRs and other systems. That leads to the development of more innovative mHealth apps and services that can seamlessly access and utilize patient data.
Patient-Centric Data Access
This growing trend toward giving patients more control over their health data involves initiatives to make health information more accessible to them. At the same time, that enables patients to contribute their data for research purposes.

As a result, tools and platforms that allow individuals to manage their health records and share them securely with healthcare providers are gaining traction. Such a shift towards patient-centric data management empowers patients, improves care coordination, and enhances patient engagement in their health management.
Interoperability in Telehealth and Remote Monitoring
As telehealth and remote patient monitoring solutions become more prevalent, healthcare data interoperability standards are being adapted to support these modalities. Integrating data from telehealth sessions and remote monitoring devices into mainstream healthcare systems is vital for continuous and coordinated care. That is also important in managing chronic conditions and providing care to populations in remote or underserved areas.
These trends highlight a dynamic and forward-looking phase in healthcare data interoperability. The focus is not only on the tech aspects of data exchange but also on transforming how care is delivered and experienced, emphasizing efficiency, patient empowerment, and innovation.
Is ensuring the proper medical data a priority for you? Our article on healthcare data quality is a must-read to discover the key elements that contribute to its accuracy!
Final Thoughts
Healthcare data interoperability is a tech endeavor and a pivotal component of a modern, efficient, and patient-centric healthcare system. Fortunately, organizations can overcome the challenges associated with it. The relevant strategy involves embracing standardized protocols, investing in compatible techs, ensuring data quality, fostering collaborative efforts, and prioritizing security and privacy.
Finally, the journey towards seamless data integration is complex and requires a concerted effort from all stakeholders in the healthcare ecosystem. However, the benefits like improved patient outcomes, enhanced efficiency, informed decision-making, and innovative solutions far outweigh the challenges.
Have questions about how to optimize your health data interoperability? Get in touch with us for expert advice and customized solutions in healthcare tech!
FAQ
What is database interoperability?
Interoperability of data and databases refers to the ability of different systems to communicate, exchange, and manage information effectively. That allows for seamless data sharing and integration across various platforms, ensuring consistency and accessibility regardless of the database technologies or formats used.
What are the benefits of data integration and interoperability?
Data integration and interoperability enhance decision-making and operational efficiency by providing comprehensive, accurate information across various systems. These processes lead to cost savings, improved data quality, and better outcomes in healthcare while ensuring compliance and facilitating collaboration.



